Emperors In Japan
It is fairly well known that Japan has had an emperor in place for centuries. While the emperor is still viewed as an important person in Japan, they do not hold the type of sovereign power they once did.
That said, they do still become involved in political affairs, though they don’t have any legislative authority.

The position of the emperor has been highly regarded in Japan, as it is believed that the very first emperor, Emperor Jimmu, was related to the goddess Amaterasu.
Amaterasu is one of the most important goddesses in Japanese mythology. For many years afterward, the succeeding emperor would be from the same bloodline as Emperor Jimmu.
The Meiji Restoration in the 1800s saw the new emperor, Meiji, take on more power than the emperors of the past.
It wasn’t until the constitution in Japan was enacted in 1947 that the emperor no longer held any significant power; instead, they are regarded as having only symbolic importance to the country.
This particular constitution brought a lot of changes to Japan and the way the government would operate in Japan, and those changes are still in effect today.
Newer Political Parties In Japan
Political parties weren’t a prominent structure in the Japanese government until they were included in their 1947 constitution. In this constitution, it was decided that people would have the freedom to form their own political parties.
This had various political parties forming in Japan. The more notable parties in the Japanese government are:
- Liberal Democratic Party
- Social Democratic Party
- New Clean Government Party
- Democratic Party Of Japan
- Japanese Communist Party
The Diet
The Diet is the formal name of the Japanese parliament. In parliament, there is the House of Representatives and the House of Councilors.
Members of these houses are elected by Japanese citizens. In order to vote in Japan, you have to be 19 years old.
Members of the House of Councilors are elected every three years, and every four years, members of the House of Representatives are elected. The Diet is responsible for enacting legislation for the entire country.

Within the House of Representatives, 300 or 480 members are elected by Japanese voters. In the House of Councilors, 96 of the 242 members are elected into their seats.
Both houses are involved in the legislative process of the government, though the House of Representatives is regarded as having more authority.
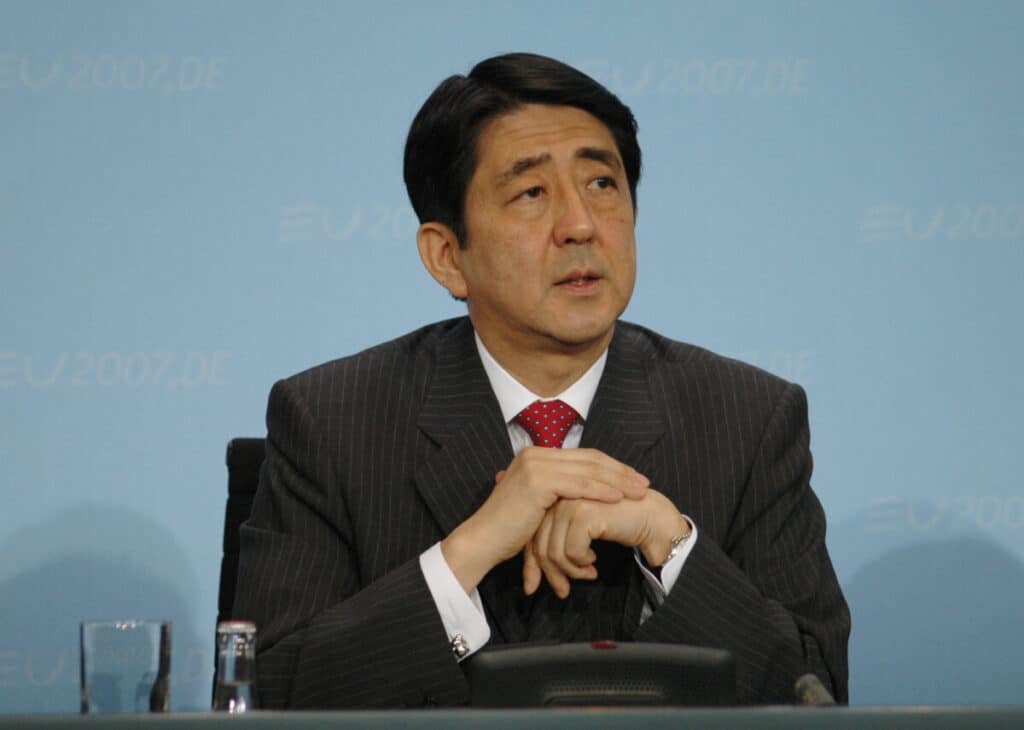
The Prime Minister
The officials within the Diet are responsible for electing the Prime Minister. The Prime Minister will then add other ministers, known as the Ministers of State, that will make up the cabinet.
There are 20 ministers that make up the cabinet alongside the Prime Minister.
The Prime Minister works alongside the Diet, and the Diet has the ultimate say in what occurs within the Japanese government.

When a bill is drafted by the cabinet, the Prime Minister will present the bill to the Diet. The Diet will then make the final decision on whether or not the bill is going to become legislation.
The Prime Minister will also liaise with the Diet on matters of national affairs as well as foreign affairs. They are also responsible for ensuring that administrative factions of the government are operating as expected.
Fumio Kishida is the current Prime Minister of Japan and has held the position since October of 2021. He is a member of the Liberal Democratic Party.
The Judicial System In Japan
Japan has several courts within its judicial system. For one to become a judge, one must be elected into the position by the cabinet of the Japanese government. The Supreme Court is the highest court in Japan.
Other courts within Japan’s judicial system include family courts, summary courts, high courts, and district courts.
Japan’s Defense System
Japan’s defense system has gone through dramatic changes throughout the country’s existence. In the current constitution, it was actually decided that Japan would no longer have a military, and they would take the stance that war was never to be initiated.
That said, Japan does technically have a military, known as the Japanese Self-Defense Forces.
In 1945, there was no defense system in place in Japan apart from the police force. When the Korean War began, Japan decided to put together the National Defense Force.

The Ministry of Defense and Security Council were, and still are, responsible for overseeing this force’s operations. The name was later changed to the Japanese Self-Defense Force.
The Japanese military also has a treaty in place with the United States. In Okinawa, there is actually a military base utilized by American troops as well as other bases on the mainland.
This treaty was put together in the 1950s as the United States helped Japan put together its military in the 1950s as a response to the Korean War.
Since the Japanese Self-Defense Force was put together, it hasn’t been involved in many conflicts or other missions.
There have been a lot of discussions internally in Japan regarding whether or not the military being in place is a violation of the constitution.
Japan’s Healthcare System
Japan is known for providing a very high quality of life for its citizens. Their healthcare system, as well as their ability to provide this quality of life, has led to overall good health for the majority of Japanese citizens as well as an increase in their life expectancy.
Those who need to access health care services benefit from widespread, national health insurance that is available to any citizen who needs to utilize it.
The government is responsible for operating some of Japan’s hospitals, while others are operated by organizations or funded by individuals.
The Distribution Of Wealth In Japan
The wealth gaps between classes in Japan used to be farther apart before the Second World War.
Various initiatives were put in place afterward that have helped create a more equal distribution of wealth within the country, including a gradual income tax system.

That said, there is still the existence of classes. Many people living in Japan fall within the middle class, of which there is an upper and a lower middle class.
There are also areas of Japan where there are pockets of poverty and homelessness, as in any country.
Social Structures And Education
Seniors and people with disabilities in Japan do also benefit from a variety of services that can assist them financially, medically, and socially.
Children and young mothers can also benefit from services that ease financial and health care burdens.
Education is also highly regarded and is taken very seriously in Japan. It’s widely believed that the quality of a person’s education is responsible for future success for those living in Japan.

It is generally expected that young people will further their education after high school by attending either college or university.
The Importance Of Culture In Government
The government has been fairly instrumental in ensuring that Japan’s cultural diversity is celebrated and safeguarded by helping to designate various sites as historically significant, thus helping to keep those sites properly maintained.
The Agency of Cultural Affairs is the government body that is responsible for making sure important parts of Japanese culture are kept safe and sacred.

While Japan has taken some influence from Chinese and Western cultures, they also have many cultural elements that have stood the test of time despite urbanization and development.










